The ICP is the world's largest global statistical initiative for estimating purchasing power parities (PPPs) to compare economic outputs, standards of living, and relative price levels across economies.
The ICP entails estimating PPPs and related macro-economic aggregates of economies for comparison. The World Bank coordinates global-level ICP, while ADB covers the program’s Asia and the Pacific component.
In 1968, United Nations Statistical Division (UNSD) and the International Comparisons Unit of the University of Pennsylvania established International Comparison Project with an ultimate goal of setting up a regular program of purchasing-power-parity-based comparisons of gross domestic product (GDP).
In 1970s, three ICP Phases were conducted with benchmark years 1970, 1973, and 1975, involving 10, 16, and 34 economies in the world, respectively. The 1970 benchmark included two ADB regional members, India and Japan; expanded the coverage to the Republic of Korea, Malaysia, the Philippines in the 1973 benchmark; and then, included Malaysia, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, and Thailand in the 1975 benchmark.
In 1980s, the ICP Phase IV (with benchmark year of 1980) and ICP Phase V (with benchmark year of 1985) significantly expanded coverage to 60 and 64 economies in the world, respectively. The 1980 benchmark covered seven ADB regional members: Hong Kong, China; India; Indonesia; Japan; the Republic of Korea; Pakistan; and Sri Lanka. Then, together with economies covered in the 1980 benchmark, four ADB regional members (Bangladesh, Nepal, the Philippines, and Thailand) were included in the succeeding 1985 benchmark year.
With a coverage of 117 economies in the world and benchmark year of 1993, only one ICP Phase was conducted in the decade of 1990s. The 1993 ICP Phase covered 13 ADB regional members: Bangladesh; Hong Kong, China; Indonesia; Japan; the Republic of Korea; the Lao People's Democratic Republic; Malaysia; Nepal; Pakistan; the Philippines; Sri Lanka; Thailand; and Viet Nam.
In its 34th session, the UN Statistical Commission launched the 2005 ICP cycle. The ICP Global Office was established at the World Bank with the primary role of coordinating the overall program under a new global governance. Covering all geographic regions of the world, five regional agencies started to directly coordinate with the statistical offices of the 146 participating economies.
Asian Development Bank assumed the role of Regional Implementing Agency (RIA) and established the Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific, coordinating with 23 participating economies. Among them, 21 are ADB regional members: Bangladesh; Bhutan; Brunei Darussalam; Cambodia; Fiji; Hong Kong, China; India; Indonesia; the Lao People's Democratic Republic; Malaysia; Maldives; Mongolia; Nepal; Pakistan; the People's Republic of China; the Philippines; Singapore; Sri Lanka; Taipei,China; Thailand; and Viet Nam. Macau, China and Islamic Republic of Iran also joined the ICP for Asia and the Pacific. This is the first time for the People's Republic of China to participate in the ICP.
Some of the ADB regional members, namely, Australia, Japan, New Zealand, and the Republic of Korea are part of the ICP undertaken by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Additionally, ADB regional members in Central Asia, namely, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Kazakhstan, the Kyrgyz Republic, and Tajikistan, are covered under the regional ICP coordinated by the Interstate Statistical Committee of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS-STAT).
Preliminary report and full report were released in 2007. Then in 2012, ADB also released a research study on the 2009 Purchasing Power Parity Update for Selected Economies in Asia and the Pacific.
The 2011 ICP round was the largest ever conducted with 177 economies participating at the full economy level. In 2016, the UN Statistical Commission established the ICP as a permanent element of the global statistical work program to be conducted regularly and more frequently. The 2017 ICP cycle covered 176 economies, or more than 99%, of the world population and the world's economic activity.
For the 2011 and 2017 ICP cycles, Asian Development Bank continued its the role as the Regional Implementing Agency (RIA) and Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific. For the 2011 and 2017 ICP cycle, 22 ADB regional members participated in ICP for Asia and the Pacific: Bangladesh; Bhutan; Brunei Darussalam; Cambodia; Fiji; Hong Kong, China; India; Indonesia; the Lao People's Democratic Republic; Malaysia; Maldives; Mongolia; Myanmar; Nepal; Pakistan; the People's Republic of China; the Philippines; Singapore; Sri Lanka; Taipei,China; Thailand; and Viet Nam. Macau, China also joined the 2011 ICP for Asia and the Pacific. The 2011 cycle is also the first time that Myanmar participated in ICP. In 2011 ICP, in addition to Fiji, the ADB member economies from the Pacific namely, Cook Islands, Kiribati, Marshall Islands, Federated States of Micronesia, Nauru, Palau, Papau New Guinea, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Tonga, Tuvalu, and Vanuatu also participated under Pacific Islands comparisons coordinated by the Australian Bureau of Statistics but their participation was limited to household consumption.
Some of the ADB regional members, namely, Australia, Japan, New Zealand, and the Republic of Korea are part of the ICP undertaken by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Additionally, ADB regional members in Central Asia, namely, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, the Kyrgyz Republic, and Tajikistan, are covered under the regional ICP coordinated by the Interstate Statistical Committee of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS-STAT). Georgia was not part of any region (singleton economy) in 2011 ICP and was linked to the CIS comparison through bilateral comparison with Armenia and in 2017 ICP was included as a guest participant in the Eurostat-OECD comparison in 2017.
The summary report and full report for the 2011 ICP for Asia and the Pacific were released in 2014. The full report and summary report along with the detailed online database for the 2017 ICP for Asia and the Pacific was released in 2020.
The latest completed ICP cycle is for the reference year 2021 in which 176 economies across the world participated. Following the UN Statistical Commission's decision in 2016 to conduct the ICP cycle every three years beginning from 2017, the ICP cycle was due in 2020. However, due to the COVID-19, the ICP Governing Board postponed the ICP cycle to reference year 2021.
For the 2021 ICP cycle, the Asian Development Bank continued its role as the Regional Implementing Agency (RIA) and Regional Office for ICP Asia and the Pacific. For this benchmark round, 21 participating ADB regional members were namely: Bangladesh; Bhutan; Brunei Darussalam; Cambodia; Fiji; Hong Kong, China; India; Indonesia; the Lao People's Democratic Republic; Malaysia; Maldives; Mongolia; Nepal; Pakistan; the People's Republic of China; the Philippines; Singapore; Sri Lanka; Taipei,China; Thailand; and Viet Nam.
The ICP includes several regions, with a Regional Implementing Agency (RIA) responsible for coordinating and implementing the program and producing regional PPPs and related results following uniform methods and standards. These RIAs are the Asian Development Bank (ADB) for Asia and the Pacific, the African Development Bank (for Africa), the Interstate Statistical Committee of the Commonwealth of Independent States (for the Commonwealth of Independent States), Eurostat (for European countries), the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) for non-European OECD countries, the United Nations Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (for Latin America and the Caribbean), and United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Western Asia (for Western Asia). The World Bank is the Global Implementing Agency that coordinates with the RIAs and compilation of global PPPs and related results by linking the regional results following established methods.
Under the ICP's global governance arrangements, ADB's regional members, who are members of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), namely, Australia, Japan, New Zealand, and the Republic of Korea, participate in the PPP comparisons led by the OECD and, hence, are not part of the ICP for Asia and the Pacific. ADB regional member economies from Central Asia, namely, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, the Kyrgyz Republic, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan participated as per the existing arrangements with the Interstate Statistical Committee of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS-STAT) as the RIA, while Georgia is included as a guest participant in the Eurostat-OECD comparison.
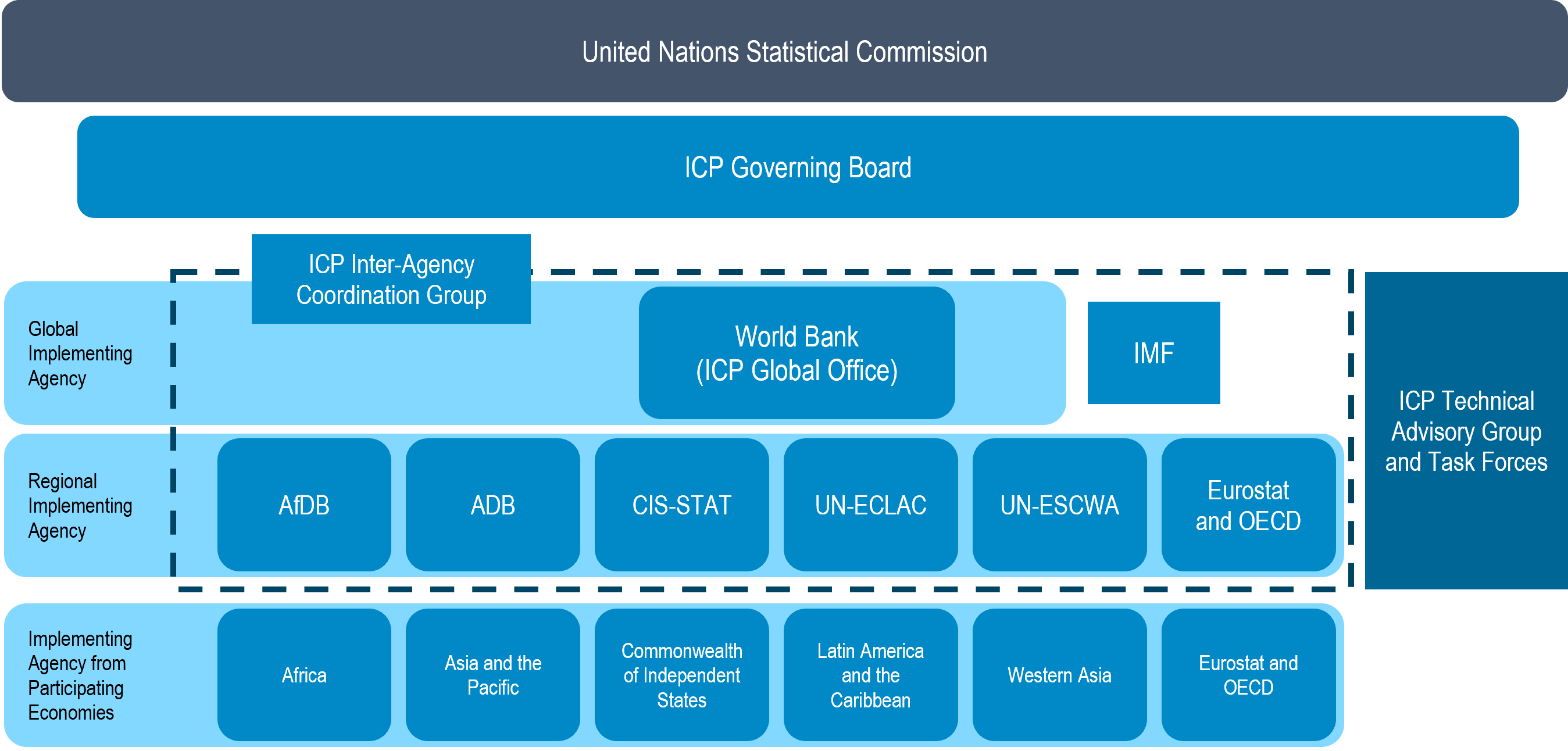 ADB = Asian Development Bank, AfDB = African Development Bank, CIS-STAT = Interstate Statistical Committee of the Commonwealth of Independent States, Eurostat = Statistical Office of the European Union, ICP = International Comparison Program, IMF = International Monetary Fund, OECD = Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, UN-ECLAC = United Nations Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean, UN-ESCWA = United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Western Asia.
ADB = Asian Development Bank, AfDB = African Development Bank, CIS-STAT = Interstate Statistical Committee of the Commonwealth of Independent States, Eurostat = Statistical Office of the European Union, ICP = International Comparison Program, IMF = International Monetary Fund, OECD = Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, UN-ECLAC = United Nations Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean, UN-ESCWA = United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Western Asia. The Governance Framework establishes the roles and responsibilities of the Governing Board (GB), the Technical Advisory Group (TAG), the ICP Global Office (GO), and the Regional Implementing Agencies (RIAs). Each of the RIAs directly works with the implementing agencies of the participating economies which are the main drivers of International Comparison Program (ICP).
Asian Development Bank (ADB), as the RIA, implements the ICP in Asia and the Pacific, receiving advice and guidance from a specially constituted Regional Advisory Board (RAB) which is composed of representatives of economy-level, regional, and global stakeholders. ADB organizes regular regional workshops, capacity-building activities, and technical assistance to the participating economies, ensuring intensive consultation of the participating economies throughout the implementation of the ICP.
The Governance Framework is extensively discussed in the website of the Global Office for the global level, and in Chapter 5 of the 2017 ICP Main Report for Asia and the Pacific.
The United Nations Statistical Commission is the ultimate stakeholder of the International Comparison Program (ICP) deciding on the frequency and operational modality of the program. The ICP Global Office reports to the UNSC every year.
The Governing Board, established by the UNSC, provides strategic leadership and is responsible for setting priorities, standards, and the work program for the ICP. The board sets the policies that govern the production of PPPs, approves methodological improvements, and conducts outreach and fundraising. It is responsible for setting up the ICP Technical Advisory Group, selecting its members, and periodically reviewing the technical research agenda and the survey and aggregation methods. It has the ultimate responsibility to review and approve any methodological innovations and methodological improvements put forward by the Technical Advisory Group. The most important function of the Governing Board is to ensure the timeliness and reliability of the results produced by the ICP following agreed policies, protocols, and methods ensuring the quality and integrity of results. The board also reviews and monitors the funding of the ICP and identifies strategies for sustained funding support for the ICP.
The Technical Advisory Group and Tasks Forces are comprised of experts in the fields of index numbers, PPPs, price statistics, and national accounts. The TAG is entrusted with ensuring methodological soundness and overall quality in the PPP estimates and steering the ICP research agenda. The group works in close coordination with the ICP Global Office and the Inter-Agency Coordination Agency to identify and resolve technical issues on the compilation of PPPs and real expenditures.
Chaired by the World Bank, the Inter-Agency Coordination Group includes the RIAs, the OECD, Eurostat, and the International Monetary Fund. The Inter-Agency Coordination Group determines activities for data collection, validation, calculation, dissemination, and capacity building at the regional level. This group has a critical role in ensuring that all the regions adhere to common standards and protocols to ensure comparability across regions and the participating economies; establishing and working on timetables and work plans for data collection, validation, compilation of results; and, finally, disseminating results.
At the recommendation of the UNSC, the World Bank has assumed permanent responsibility for the ICP Global Office, responsible for global coordination and implementation of the ICP. It organizes and conducts meetings of the Inter-Agency Coordination Group and acts as its secretariat, responsible for day-to-day management, serves as the secretariat to the Governing Board and the Technical Advisory Group, and prepares submissions and annual reports to the UNSC.
The Regional Implementing Agencies carry out day-to-day management of the regional programs; plan and implement the regional ICP activities in line with the agreed timetables; ensure the quality of economy level and regional data and metadata; and conduct regular workshops on the preparation of item lists, regional validation of data, and the assessment of the ICP results for the region. The RIAs are also responsible for capacity-building activities within the region and provide technical assistance to the participating economies on the conduct of price surveys and subsequent validation of data. They provide the ICP Global Office with economy level and regional data and metadata for purposes of analysis and validation at the global level and for linking the regional results to calculate global results. The organizations acting as the RIAs are the:
In the ICP for Asia and the Pacific, the Regional Advisory Board is established to provide advice to the ICP Asia and the Pacific regional coordinator. The board includes representatives of economy-level and regional stakeholders. RAB is not an executive body nor involved in the day-to-day management of the ICP. Its roles are: to set regional goals, objectives, and priorities; to guide work program prepared by the regional coordinator who is responsible for the day-to-day management of the regional program; to review ICP progress and provide guidance in timely implementing ICP activities in line with methods prescribed by the Technical Advisory Group for the ICP and global practices; and provide guidance on the future direction of ICP in the region.
The implementing agencies of the participating economies are responsible for ICP activities at the economy level. They are responsible for coordinating and implementing the ICP work program established at the regional level. As the timeliness and quality of price and national accounts data are fundamental to the ICP, the implementing agency in each economy plays a vital role in ensuring that the ICP surveys are conducted in a timely manner and quality assurance standards as prescribed by the regional coordinator are met. They are responsible for collecting and compiling data and metadata necessary for compiling PPPs and real expenditures. They periodically submit the data to their RIA and actively participate in regional workshops to discuss ICP operational guidelines and survey materials, undertake data validation, examine data and metadata quality, and to discuss preliminary and final ICP results for the region.
The ICP is the world's largest global statistical initiative for estimating purchasing power parities (PPPs) to compare economic outputs, standards of living, and relative price levels across economies.
View ICP governance
These present the ICP reports and related research presenting methodologies and results of purchasing power parities (PPPs) across various ICP cycles in Asia and the Pacific and related research such as studies on poverty-specific PPPs, integrating ICP with the Consumer Price Index as a framework for subnational PPPs, and alternative approaches for estimating PPPs for non-benchmark years in the region.
ICP Reports and Research NEWGuide on the Integration of CPI and ICP Activities
ICP COVID-19 Guidance Note on Price Surveys
ICP COVID-19 Guidance Note on National Accounts
Expenditure Data
